
MediDrop® Sucralose: Delivery Solution for Extended Treatments
ClearH2O’s medication delivery product line provides researchers and veterinarians with solutions for a variety of animal needs, from standard husbandry treatments to compound testing. MediDrop® Sucralose is a liquid gel, containing less than 1% sucralose and packaged in one gallon containers. It is ready to use, directly replacing the water in the cage water bottle. It is convenient for extended treatments, as it can be left untouched in the water bottle for 7 days. The greatest advantage of using MediDrop® Sucralose in lieu of water in the water bottle is that, due to its viscosity, it keeps the medication in suspension, eliminating the need to shake the water bottle daily, and distributing higher and steadier drug levels to the animals.
MediDrop® Sucralose for Antibiotic Delivery
Two studies, conducted by independent research institutes, showed that MediDrop® Sucralose for the delivery of the antibiotic TMS (sulfamethoxazole/trimethoprim; known notably under the brand names Bactrim® or Sulfatrim®) was a superior method of delivery compared to water. The blood levels of the drugs were higher and steadier in the mice who received the drugs through MediDrop® Sucralose compared to those who received it via water.
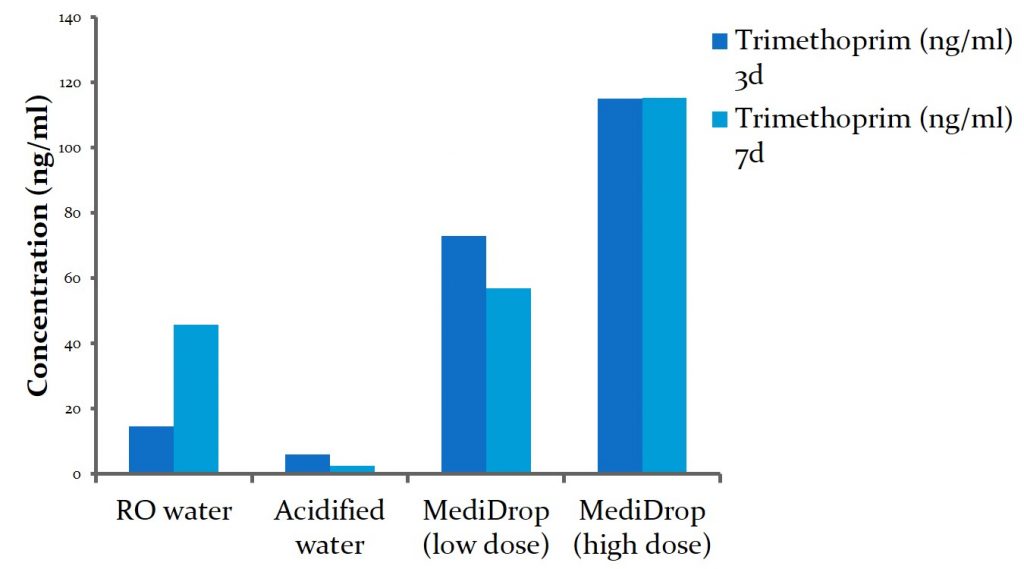
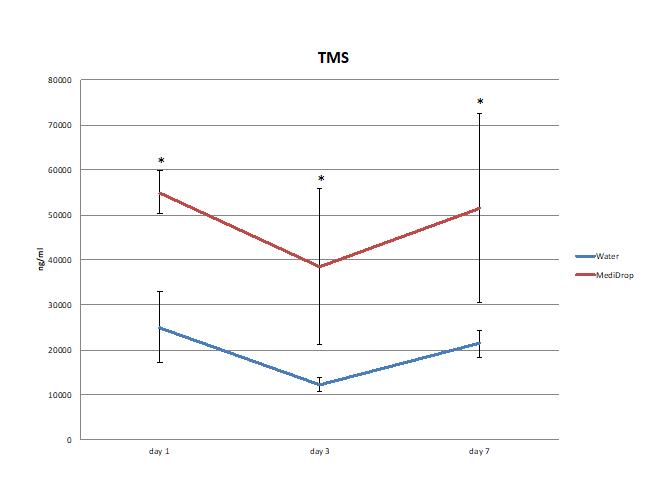
Check out the 2 studies in our blog post on antibiotics delivery through MediDrop® Sucralose:
Are Your Mice Getting The Correct Dose of Antibiotics?
Rethinking the use of Water for Medication Delivery
MediDrop® Sucralose for Analgesic Delivery
Providing analgesics to laboratory animals in pain is an ethical obligation required to be in compliance with the 3Rs, a framework for performing more humane animal research which is embedded in international legislation and regulations on the use of animals in scientific procedures, such as the Animal Welfare Act (1)

Every effort should be made to minimize any pain or distress that animals experience during scientific procedures. In addition to compromising animal welfare, pain is a source of stress that can cause undesirable effects on the outcome of research projects (2). Several viable options exist to relieve pain in laboratory animals (3):
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs): Carprofen, meloxicam, ketoprofen …
- Antipyretics: Acetominophen, aspirin …
- Opioids: Buprenorphine, fentanyl, morphine, tramadol …
On their own, each drug can be used to moderate pain of mild to moderate intensity either after minor procedures (blood samples, biopsies) or after major procedures (any procedure that penetrates and exposes a body cavity). Pre-emptive analgesia, the administration of analgesics agent before the painful procedure, should be provided whenever possible, as it prevents the sensitization of the nervous system, and help reduce post-operative pain (4, 5). Multimodal analgesia, which involves different classes of analgesics and/or different sites of drug administration, results in an additive effect, and a maximization of the analgesic effect, and is suitable for severe pain.
In a 2019 study (PMID 30674967), a Canadian group from the University of Toronto used MediDrop® Sucralose to administer 3 different analgesics pre- and post-surgery: Carprofen (10 and 25mg/kg), meloxicam (2 and 5mg/kg), and buprenorphine (0.1mg/kg), and observed statistically significant reductions in pain scores for all drugs.
MediDrop® Sucralose for Infectious Disease Treatment Delivery
Infectious diseases are disorders caused by pathogens such as bacteria, fungi, viruses or parasites. They are extremely common. Symptoms range from mild to severe, and treatment depends on the cause of the illness. Transmission may occur in a variety of ways, including direct contact, water or food, air and through insects. Infectious disease research aims to find ways to diagnose, treat and prevent infectious diseases. Some of the most common infectious diseases are:
- HIV (human immunodeficiency virus) is a virus that attacks the body’s immune system, and can lead to AIDS if untreated (acquired immunodeficiency syndrome). Two studies published in 2018 by the City of Hope in CA, USA (PMID 29343582 and PMID 29556342) used MediDrop® Sucralose to deliver a treatment of combinatorial antiretroviral therapy (cART), an effective therapeutics for HIV, to HIV-infected hu-NSG mice for 2 to 6 weeks. The ART regimen consisting of tenofovir disoproxil fumarate (TDF; 300 mg/capsule), emtricitabine (FTC; 200 mg/capsule) and raltegravir (RAL; 400 mg/capsule). The medication tablets were powdered thoroughly and re-suspended in the sweetened water gel formulation. The study demonstrated that this regimen can reliably suppress viremia.
- EBV (Epstein-Barr virus) is a member of the herpes virus family. It is extremely common, and most people get infected with EBV at some point in their lives, but might not develop any symptoms. However, EBV can cause mononucleosis and is associated with certain cancers and lymphomas. In 2020, a study from University of Zürich in Switzerland (PMID 32576602) aimed to study the EBV-HIV coinfection, which V is the norm rather than an exception for people infected with HIV. cART consisted of abacavir (ABC) (100 mg/kg/day), lamivudine (3TC) (150 mg/kg/day), and dolutegravir (DTG) (15 mg/kg/day) pills reduced to powder and solubilized in MediDrop® Sucralose
- HBV (Hepatitis B virus) causes liver infection, inflammation and damage. Two studies were published in 2020: the first one, from Institut Pasteur in Paris, France (PMID 32579155) delivered Entecavir (ETV) at 0.3 mg/kg/day, an antiviral medication used in the treatment of HBV, through MediDrop® Sucralose for 3 weeks. In the second study, led by a group at Emory University, GA, USA, (PMID 31712213), HBV-infected mice were treated with either ETV (0.3 mg/kg/day) , GLP-26 (60 mg/kg/day), or the combination of ETV/GLP-26 at the same doses, delivered in MediDrop® Sucralose continuously for 10 weeks.
MediDrop® Sucralose can be used to deliver a variety of drugs and compounds.
Are you using drugs in ClearH2O gels that are not listed here ? Contact us!
To try a sample, fill out a request here
References:
(1) The Animal Welfare Act Blue Book
(2) Analgesia – NC3Rs
(3) Analgesia Guidelines – University of Minnesota
(4) Analgesia Guidelines – University of Iowa
(5) Guide for the Use and Care of Laboratory Animals
Image from Agenda Life Sciences
To access the full text of the 6 articles mentioned, please refer to our Resource Section
To learn more about ClearH2O’s medication delivery solutions, check out our Medication Delivery Blog Series and visit our Medication delivery webpage

